We believe strongly that we can and must do something different.
Our aim is to make your ideas come true.
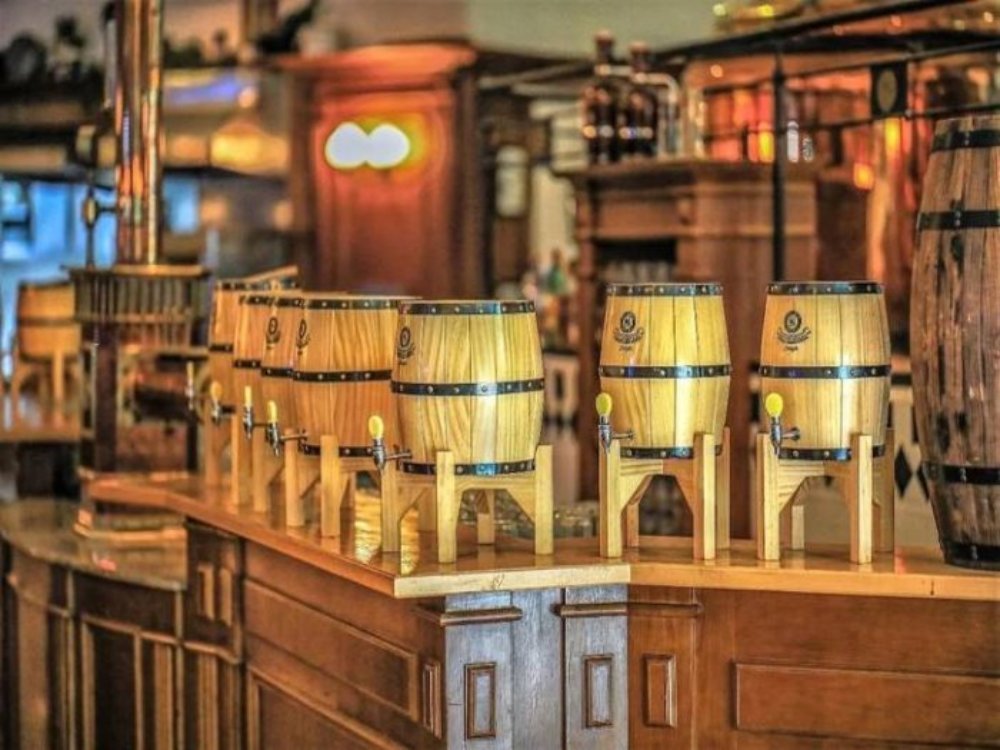
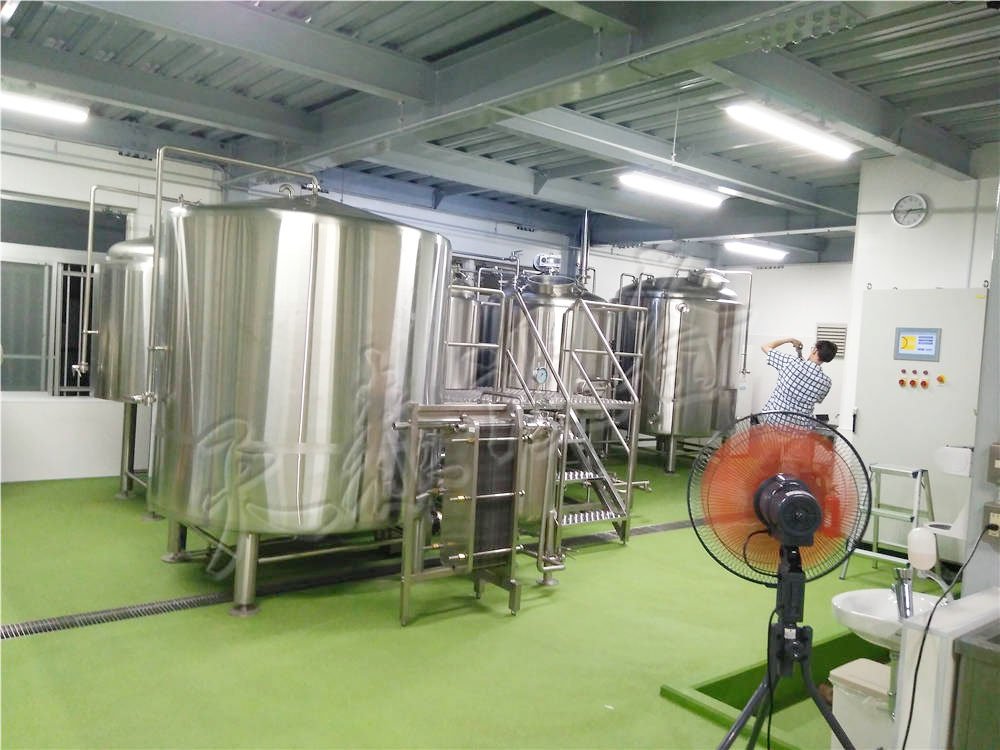
Brewery Setup Blog
Do something for your dream.
Start from selection
Location
CN Jinan- 2668
Jichang Rd.
Email Us
Call Center
24/7 Support
+86 531 88161066












Request A Quote